Dna fingerprinting is a quicker way to compare the sequences of two individuals.
What is satellite dna in a genome explain their role in dna fingerprinting.
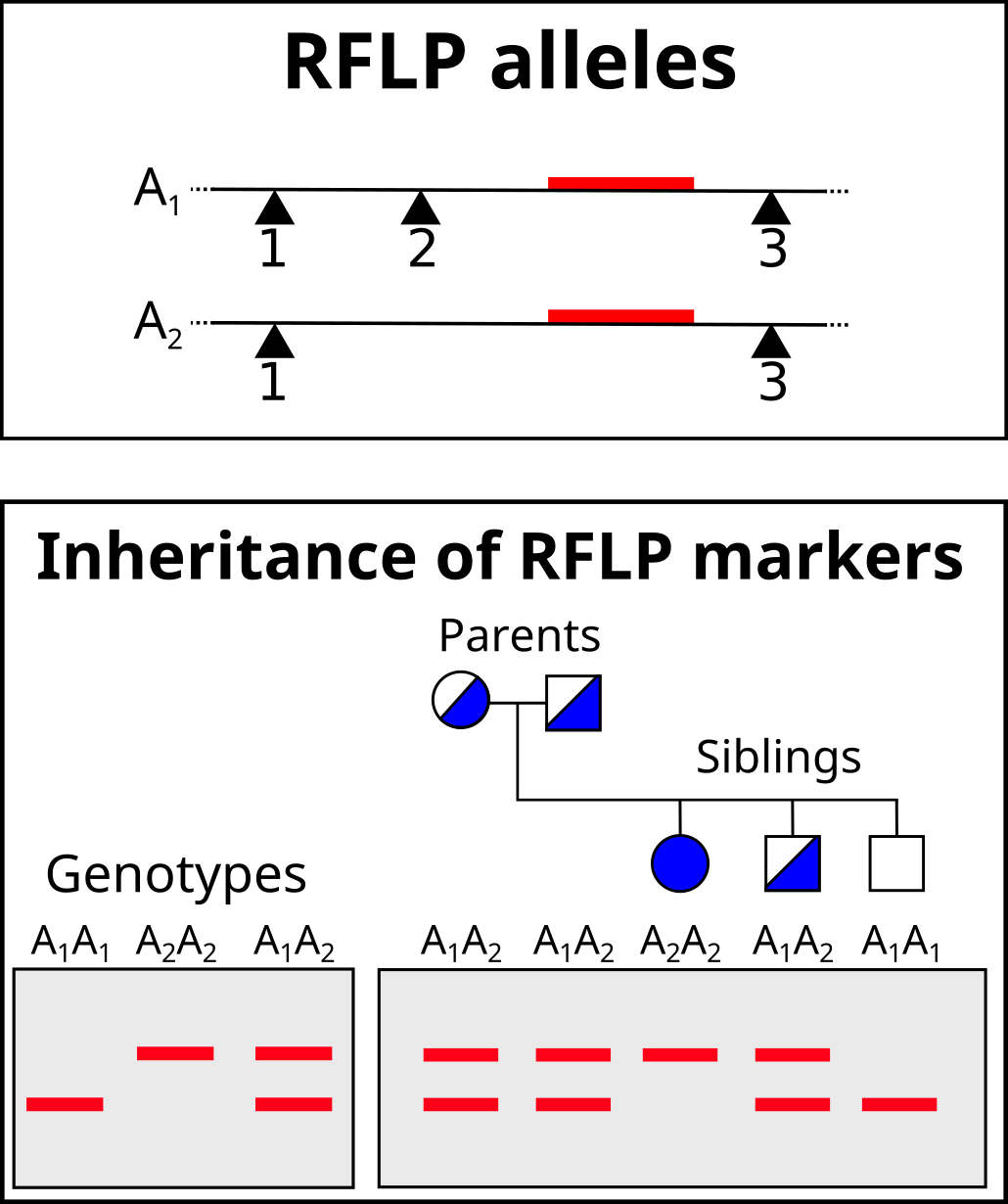
Each variant acts as an inherited allele allowing them to be used for personal or parental identification.
Significance of satellite dna in dna fingerprinting a dna satellite is a region that consists of short dna sequences repeated many times.
The variation between individuals in the lengths of their dna satellites forms the basis of dna fingerprinting.
Although popularly satellite dna is thought to be part of junk dna or selfish dna which occupy the genome but have no effect on the fitness of an organism recent studies show several distinct.
Satellite dna regions are stretches of repetitive dna which do not code for any specific protein.
This technique involves identifying differences in the repetitive dna regions.
Dna fingerprinting was invented in 1984 by professor sir alec jeffreys after he realised you could detect variations in human dna in the form of these minisatellites.
They depict a high level of polymorphism and are the basis of dna fingerprinting.
These non coding sequences form a major chunk of the dna profile of humans.
Explain the significance of satellite dna in dna fingerprinting technique.
Their analysis is useful in genetics and biological research forensics and dna fingerprinting.
The peaks on a density gradient centrifugation help to separate the repetitive part from the bulk dna.
Ncert p bahadur iit jee previous year narendra awasthi ms chauhan.
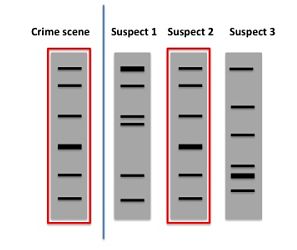
This is a dna fingerprint.
The name satellite dna refers to the phenomenon that repetitions of a short dna sequence tend to produce a different frequency of the bases adenine cytosine guanine and thymine and thus have a different density from bulk dna such that they form a second or satellite band when genomic d.
The variation between individuals in the lengths of their dna satellites forms the basis of dna fingerprinting.
Here the bulk dna forms a major peak while the small peaks are called satellite dna.
Dna fingerprinting also called dna typing dna profiling genetic fingerprinting genotyping or identity testing in genetics method of isolating and identifying variable elements within the base pair sequence of dna deoxyribonucleic acid.
Satellite dna consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating non coding dna.
It belongs to a class of satellite dna.
The number of copies of nucleotide differs from chromosome to chromosome in an individual.
Dna fingerprinting is a technique that simultaneously detects lots of minisatellites in the genome to produce a pattern unique to an individual.
Satellite dna is the main component of functional centromeres and form the main structural constituent of heterochromatin.
Satellite dna are dna sequences that contain highly repetitive dna which means that a single sequence is repeated many times over.